segment
Divides a cube object into multiple output cubes in the line direction.
Note: The output cubes (which will here on be referred to as segments) will be created in the naming form of (InputCubeName).segment(#).cub
i.e. peaks.segment1.cub, peaks.segment2.cub, peaks.segment3.cub, peaks.segment4.cub, etc
Categories
History
| Christopher Austin | 2007-10-30 | Original version |
Parameters
Files
| Type | cube |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Filter | *.cub |
Output Parameters
| Type | integer |
|---|
| Type | integer |
|---|
Example 1
Segmented Peaks
Command Line
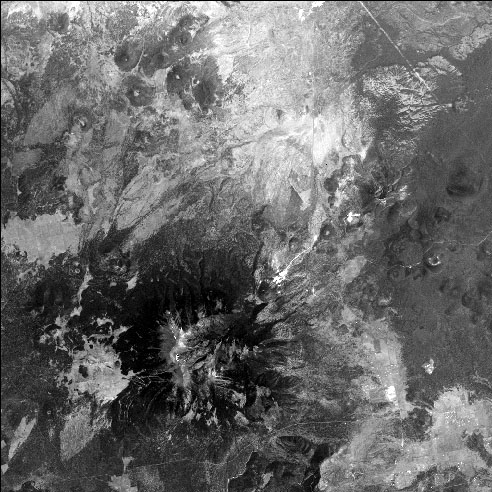
segment FROM=peaks.cub NL=531 OVERLAP=88
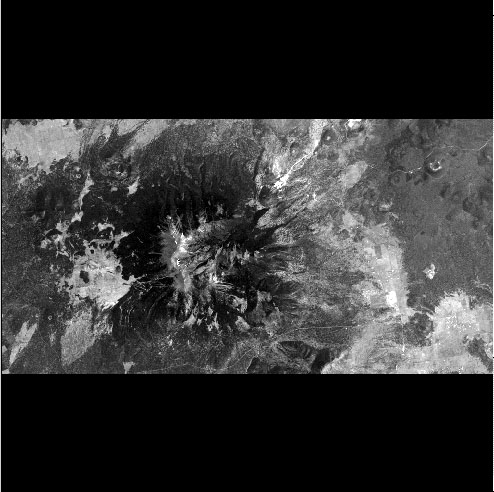
Input Image
Output Images
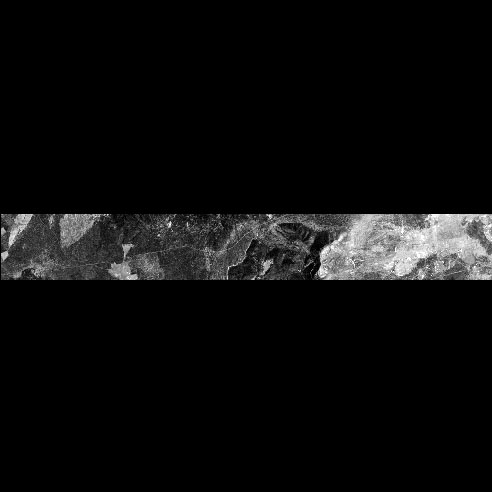
The first segment.
peaks.segment1.cubThis is the first segment created from peaks.cub
It has the same sample width and band depth as peaks.cub, and has a total number of lines equal to the NL parameter, which is 531 in this example.
The second segment.
peaks.segment2.cubThis is the second segment created from peaks.cub
Like peaks.segment1.cub, it has 531 lines and the same sample width and band depth as peaks.cub. The first 88 lines of this cube (peaks.segment2.cub) are identical to the last 88 lines of its previous cube (peaks.segment1.cub). In the same manner, the last 88 lines of peaks.segment2.cub are identical to the first 88 lines of peaks.segment3.cub
The third segment.
peaks.segment3.cubThis is the third segment created from peaks.cub
Notice how this segment is smaller than the other 2 segements. This is due to the fact that it reached the end of peaks.cub, nevertheless, it still has the same
sample width and band depth as peaks.cub
This shortening of the segment will only happen in the final segment created from the input cube.