 |
Isis Developer Reference
|
 |
Isis Developer Reference
|
Base class for Map Projections. More...
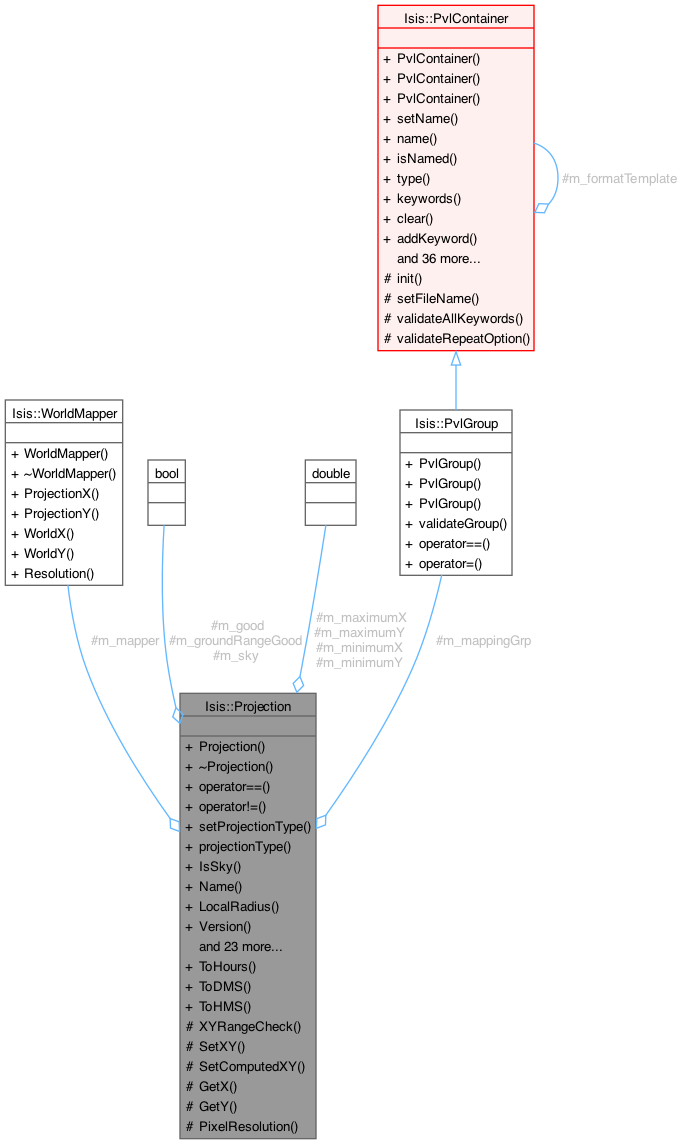
#include <Projection.h>
Public Types | |
| enum | ProjectionType { Triaxial , RingPlane } |
| This enum defines the subclasses of Projection supported in Isis. More... | |
Public Member Functions | |
| Projection (Pvl &label) | |
| Constructs an empty Projection object. | |
| virtual | ~Projection () |
| Destroys the Projection object. | |
| virtual bool | operator== (const Projection &proj) |
| This method determines whether two map projection objects are equal by comparing the resolution, and projection name. | |
| bool | operator!= (const Projection &proj) |
| This method determines whether two map projection objects are not equal. | |
| void | setProjectionType (const ProjectionType ptype) |
| Sets the projection subclass type. | |
| ProjectionType | projectionType () const |
| Returns an enum value for the projection type. | |
| bool | IsSky () const |
| Returns true if projection is sky and false if it is land. | |
| virtual QString | Name () const =0 |
| This method returns the name of the map projection. | |
| virtual double | LocalRadius () const =0 |
| virtual QString | Version () const =0 |
| This method returns the Version of the map projection. | |
| virtual bool | IsEquatorialCylindrical () |
| This method returns true if the projection is equatorial cylindrical. | |
| virtual bool | HasGroundRange () const |
| This indicates if the longitude direction type is positive west (as opposed to postive east). | |
| double | Rotation () const |
| Returns the value of the Rotation keyword from the mapping group. | |
| void | SetWorldMapper (WorldMapper *mapper) |
| If desired the programmer can use this method to set a world mapper to be used in the SetWorld, WorldX, and WorldY methods. | |
| virtual bool | SetGround (const double lat, const double lon)=0 |
| virtual bool | SetCoordinate (const double x, const double y)=0 |
| bool | IsGood () const |
| This indicates if the last invocation of SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld was with successful or not. | |
| double | XCoord () const |
| This returns the projection X provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success. | |
| double | YCoord () const |
| This returns the projection Y provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success. | |
| virtual bool | SetUniversalGround (const double coord1, const double coord2) |
| This method is used to set the lat/lon or radius/azimuth (i.e. | |
| virtual bool | SetUnboundUniversalGround (const double coord1, const double coord2) |
| This method is used to set the lat/lon or radius/azimuth (i.e. | |
| virtual bool | SetWorld (const double x, const double y) |
| This method is used to set a world coordinate. | |
| virtual double | WorldX () const |
| This returns the world X coordinate provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success. | |
| virtual double | WorldY () const |
| This returns the world Y coordinate provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success. | |
| double | ToWorldX (const double projectionX) const |
| This method converts a projection x value to a world x value. | |
| double | ToWorldY (const double projectionY) const |
| This method converts a projection y value to a world y value. | |
| double | ToProjectionX (const double worldX) const |
| This method converts a world x value to a projection x value. | |
| double | ToProjectionY (const double worldY) const |
| This method converts a world y value to a projection y value. | |
| double | Resolution () const |
| This method returns the resolution for mapping world coordinates into projection coordinates. | |
| virtual double | Scale () const =0 |
| virtual bool | XYRange (double &minX, double &maxX, double &minY, double &maxY)=0 |
| void | SetUpperLeftCorner (const Displacement &x, const Displacement &y) |
| This method searches for extreme (min/max/discontinuity) coordinate values along the constBorder line between minBorder and maxBorder (that is, across latitudes/longitudes). | |
| virtual PvlGroup | Mapping ()=0 |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static double | ToHours (double angle) |
| Converts the given angle (in degrees) to hours by using the ratio 15 degrees per hour. | |
| static QString | ToDMS (double angle) |
| Converts the given angle (in degrees) to degrees, minutes, seconds. | |
| static QString | ToHMS (double angle) |
| Converts the given angle (in degrees) to hours, minutes, seconds. | |
Protected Member Functions | |
| virtual void | XYRangeCheck (const double latitude, const double longitude)=0 |
| void | SetXY (double x, double y) |
| This protected method is a helper for derived classes. | |
| void | SetComputedXY (double x, double y) |
| This protected method is a helper for derived classes. | |
| double | GetX () const |
| Calculates the unrotated form of current x value. | |
| double | GetY () const |
| Calculates the unrotated form of the current y value. | |
| double | PixelResolution () const |
| Returns the pixel resolution value from the PVL mapping group in meters/pixel. | |
Protected Attributes | |
| WorldMapper * | m_mapper |
| This points to a mapper passed into the SetWorldMapper method. | |
| bool | m_good |
| Indicates if the contents of m_x, m_y, m_latitude, and m_longitude are valid. | |
| bool | m_sky |
| Indicates whether projection is sky or land. | |
| bool | m_groundRangeGood |
| Indicates if the ground range (min/max lat/lons) were read from the labels. | |
| double | m_minimumX |
| The data elements m_minimumX, m_minimumY, m_maximumX, and m_maximumY are convience data elements when you write the XYRange virtual function. | |
| double | m_maximumX |
| See minimumX description. | |
| double | m_minimumY |
| See minimumX description. | |
| double | m_maximumY |
| See minimumX description. | |
| PvlGroup | m_mappingGrp |
| Mapping group that created this projection. | |
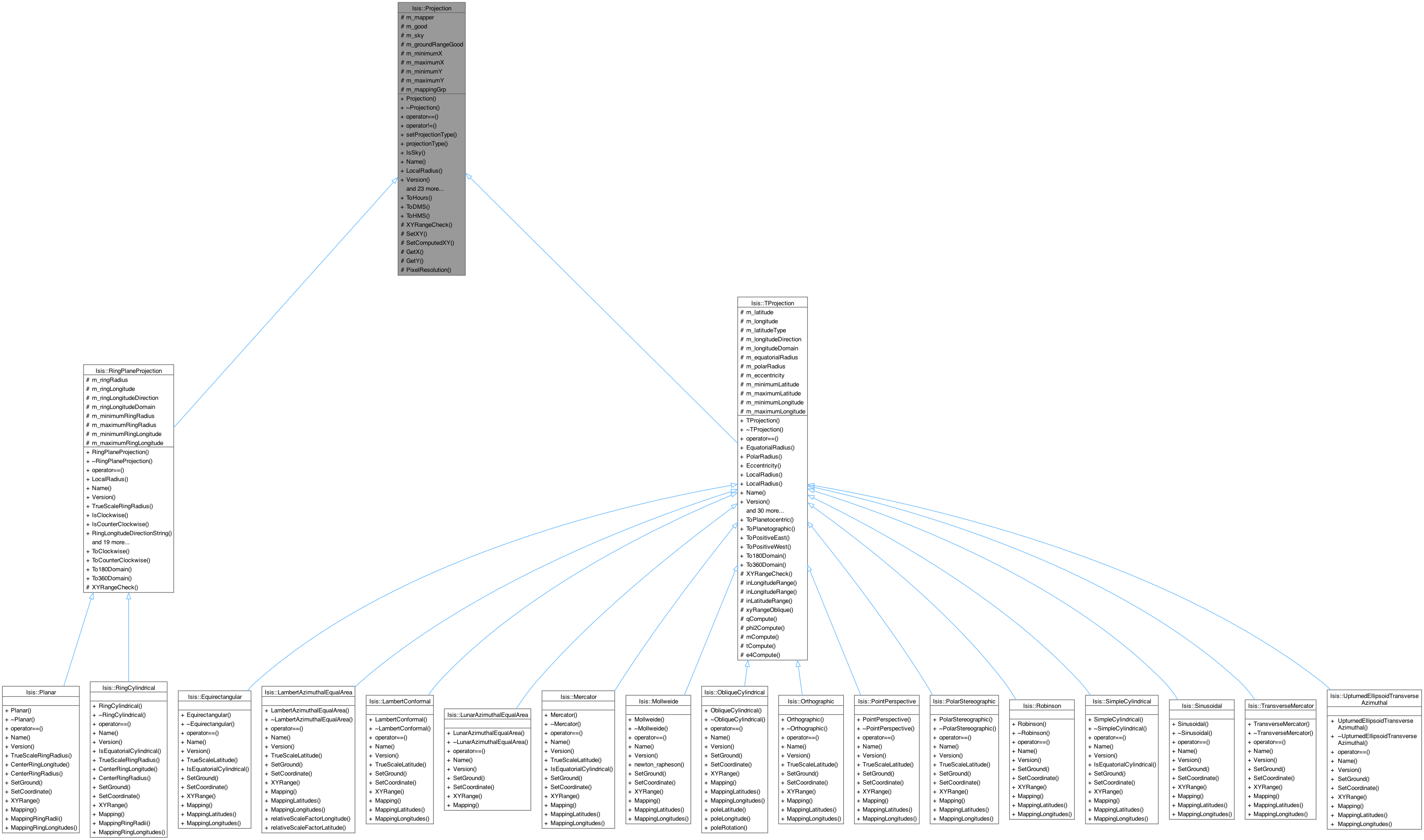
Base class for Map Projections.
This is a virtual base class for map projections. It must be used to create specific map projection classes such as Sinusoidal, Mercator, etc. The foundation of this class is the ability to convert ground coordinates (latitude and longitude) into projection coordinates (x and y) and vice versa. Options exist to allow conversion to and from programmer specified world coordinates. The world coordinates can be cube pixels, paper units in millimeters, or any other unit the program may need. Generally, you should never directly instantiate this class.
Here is an example of how to use Projection
If you would like to see Projection being used in implementation, see mappos.cpp
This enum defines the subclasses of Projection supported in Isis.
| Enumerator | |
|---|---|
| Triaxial | These projections are used to map triaxial and irregular-shaped bodies. |
| RingPlane | These projections are used to map ring planes. |
| Isis::Projection::Projection | ( | Pvl & | label | ) |
Constructs an empty Projection object.
| label | A PVL object containing map projection labels. These labels are fully described in the Isis Map Projection Users Guide. A brief example follows: Group = Mapping
EquatorialRadius = 3396190.0
PolarRadius = 3376200.0
LongitudeDirection = PositiveEast
LongitudeDomain = 360
LatitudeType = Planetographic
MinimumLatitude = 10.8920539924144
MaximumLatitude = 34.7603960060206
MinimumLongitude = 219.72432466275
MaximumLongitude = 236.186050244411
PixelResolution = 1387.31209461362
ProjectionName = SimpleCylindrical
CenterLongitude = 220.0
EndGroup
End
double PixelResolution() const Returns the pixel resolution value from the PVL mapping group in meters/pixel. Definition Projection.cpp:840 virtual PvlGroup Mapping()=0 |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. No target radii available through keywords [EquatorialRadius and PolarRadius] or [TargetName]." |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid value for keyword [EquatorialRadius]. It must be greater than zero." |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid value for keyword [PolarRadius]. It must be greater than zero." |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid value for keyword [LatitudeType] must be [Planetographic or Planetocentric]" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid value for keyword [LongitudeDirection] must be [PositiveWest or PositiveEast]" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid value for keyword [LongitudeDomain] must be [180 or 360]" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. [MinimumLatitude] is outside the range of [-90:90]" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. [MaximumLatitude] is outside the range of [-90:90]" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. [MinimumLatitude,MaximumLatitude] are not properly ordered" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. [MinimumLongitude,MaximumLongitude] are not properly ordered" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid keyword value(s). [EquatorialRadius] must be greater than or equal to [PolarRadius]" |
| IException::Unknown | - "Projection failed. Invalid label group [Mapping]" |
References _FILEINFO_, Isis::PvlObject::findGroup(), Isis::PvlContainer::hasKeyword(), m_good, m_mapper, m_mappingGrp, m_maximumX, m_maximumY, m_minimumX, m_minimumY, m_sky, Isis::Null, Isis::PvlObject::Traverse, and Isis::IException::Unknown.
|
virtual |
Destroys the Projection object.
References m_mapper.
|
protected |
Calculates the unrotated form of current x value.
References Isis::PI.
Referenced by Isis::Equirectangular::SetCoordinate(), Isis::LambertConformal::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Mercator::SetCoordinate(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Orthographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PointPerspective::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PolarStereographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::RingCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Sinusoidal::SetCoordinate(), and Isis::TransverseMercator::SetCoordinate().
|
protected |
Calculates the unrotated form of the current y value.
References Isis::PI.
Referenced by Isis::Equirectangular::SetCoordinate(), Isis::LambertConformal::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Mercator::SetCoordinate(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Orthographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PointPerspective::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PolarStereographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::RingCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Sinusoidal::SetCoordinate(), and Isis::TransverseMercator::SetCoordinate().
|
virtual |
This indicates if the longitude direction type is positive west (as opposed to postive east).
The longitude type was obtained from the label during object construction.
| lon | Longitude to convert into the -180 to 180 domain. |
| IException::Unknown | - "The given longitude is invalid." |
| lon | Longitude to convert into the 0 to 360 domain. |
References m_groundRangeGood.
Referenced by Isis::RingPlaneProjection::Mapping(), Isis::TProjection::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::TProjection::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::Planar::MappingRingLongitudes(), Isis::RingCylindrical::MappingRingLongitudes(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::MappingRingLongitudes(), Isis::Planar::MappingRingRadii(), Isis::RingCylindrical::MappingRingRadii(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::MappingRingRadii(), and Isis::TProjection::xyRangeOblique().
|
virtual |
This method returns true if the projection is equatorial cylindrical.
In other words, if the projection is cylindrical and an image projected at 0 is the same as an image projected at 360.
Reimplemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::Mercator, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, and Isis::TProjection.
Referenced by Isis::ShapeModelFactory::create().
| bool Isis::Projection::IsGood | ( | ) | const |
This indicates if the last invocation of SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld was with successful or not.
If there was success then the Latitude, Longitude, XCoord, YCoord, UniversalLatitude, UniversalLongitude, WorldX, and WorldY methods can be utilized.
References m_good.
Referenced by Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck().
| bool Isis::Projection::IsSky | ( | ) | const |
Returns true if projection is sky and false if it is land.
References m_sky.
Referenced by Isis::Camera::SetImage(), Isis::Camera::SetImage(), and Isis::Camera::SetRightAscensionDeclination().
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::RingPlaneProjection, and Isis::TProjection.
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::Planar, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::RingPlaneProjection, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TProjection, Isis::TransverseMercator, and Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal.
Referenced by Isis::MosaicSceneWidget::addToPermanent(), Isis::MosaicGridToolConfigDialog::applySettings(), Isis::GroundGrid::GroundGrid(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::GroundRange(), Isis::MosaicGridToolConfigDialog::readSettings(), Isis::MosaicSceneWidget::save(), and Isis::MosaicSceneWidget::toPvl().
|
pure virtual |
This method returns the name of the map projection.
It is a pure virtual method (requires all subclasses to override).
Implemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::Planar, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TransverseMercator, Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal, Isis::RingPlaneProjection, and Isis::TProjection.
Referenced by operator==().
| bool Isis::Projection::operator!= | ( | const Projection & | proj | ) |
This method determines whether two map projection objects are not equal.
True is returned if they have at least some differences in the radii, latitude type, longitude direction, resolution, or projection name.
| proj | A reference to a Projection object to which this Projection will be compared. |
|
virtual |
This method determines whether two map projection objects are equal by comparing the resolution, and projection name.
| proj | A reference to a Projection object to which this Projection will be compared. |
Reimplemented in Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::Planar, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::RingPlaneProjection, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TProjection, Isis::TransverseMercator, and Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal.
References Name(), and Resolution().
|
protected |
Returns the pixel resolution value from the PVL mapping group in meters/pixel.
Referenced by Isis::Planar::XYRange(), and Isis::RingCylindrical::XYRange().
| Projection::ProjectionType Isis::Projection::projectionType | ( | ) | const |
Returns an enum value for the projection type.
Referenced by Isis::MosaicFindTool::getUserGroundPoint(), Isis::GridGraphicsItem::GridGraphicsItem(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::GroundRange(), Isis::MosaicControlNetTool::mouseButtonRelease(), Isis::MosaicFindTool::mouseButtonRelease(), SetUnboundUniversalGround(), SetUniversalGround(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::UniversalLatitude(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::UniversalLongitude(), and Isis::MosaicAreaTool::userChangedBox().
| double Isis::Projection::Resolution | ( | ) | const |
This method returns the resolution for mapping world coordinates into projection coordinates.
For example, if the world coordinate system is an image then this routine returns the number of meters per pixel. Likewise, if the world coordinate system is a piece of paper, it might return the number of meters per inch of paper. If the SetWorldMapper method is not invoked then this method returns 1.0
References m_mapper, and Isis::WorldMapper::Resolution().
Referenced by operator==(), and Isis::UniversalGroundMap::Resolution().
| double Isis::Projection::Rotation | ( | ) | const |
Returns the value of the Rotation keyword from the mapping group.
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::RingPlaneProjection, and Isis::TProjection.
|
protected |
This protected method is a helper for derived classes.
It takes unrotated x and y values, rotates them using the rotation angle data member, and stores the results in the current x and y data members.
| x | The unrotated x coordinate. |
| y | The unrotated y coordinate. |
References m_good, Isis::Null, and Isis::PI.
Referenced by Isis::Equirectangular::SetGround(), Isis::LambertConformal::SetGround(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::SetGround(), Isis::Mercator::SetGround(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::SetGround(), Isis::Orthographic::SetGround(), Isis::PointPerspective::SetGround(), Isis::PolarStereographic::SetGround(), Isis::Robinson::SetGround(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::SetGround(), Isis::Sinusoidal::SetGround(), Isis::TProjection::SetGround(), Isis::TransverseMercator::SetGround(), Isis::Planar::SetGround(), Isis::RingCylindrical::SetGround(), and Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetGround().
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::Planar, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::RingPlaneProjection, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TProjection, Isis::TransverseMercator, and Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal.
Referenced by SetWorld().
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TProjection, Isis::TransverseMercator, Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal, Isis::Planar, Isis::RingCylindrical, and Isis::RingPlaneProjection.
Referenced by Isis::Camera::SetRightAscensionDeclination().
| void Isis::Projection::setProjectionType | ( | const ProjectionType | ptype | ) |
Sets the projection subclass type.
| ptype | The projection subclass type |
Referenced by Isis::RingPlaneProjection::RingPlaneProjection(), and Isis::TProjection::TProjection().
|
virtual |
This method is used to set the lat/lon or radius/azimuth (i.e.
ring longitude) coordinate, depending on the projection type. The Set forces an attempted calculation of the projection X/Y values. This may or may not be successful and a status is returned as such. This method will not adjust the longitude coordinate based on the longitude domain.
| coord1 | Latitude (planetocentric) or ring radius to project |
| coord2 | Longitude or ring longitude to project. The value passed in should be PositiveEast, Domain360. |
Reimplemented in Isis::TProjection.
References m_good, Isis::Null, projectionType(), Isis::TProjection::SetUnboundUniversalGround(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetUniversalGround(), and Triaxial.
Referenced by Isis::UniversalGroundMap::SetUnboundGround().
|
virtual |
This method is used to set the lat/lon or radius/azimuth (i.e.
ring longitude) coordinate, depending on the projection type. The Set forces an attempted calculation of the projection X/Y values. This may or may not be successful and a status is returned as such.
| coord1 | Latitude (planetocentric) or ring radius to project |
| coord2 | Longitude or ring longitude to project. The value passed in should be PositiveEast, Domain360. |
Reimplemented in Isis::TProjection, and Isis::RingPlaneProjection.
References m_good, Isis::Null, projectionType(), Isis::TProjection::SetUniversalGround(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetUniversalGround(), and Triaxial.
Referenced by Isis::DemShape::localRadius(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::SetGround(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::SetGround(), Isis::Camera::SetRightAscensionDeclination(), and Isis::UniversalGroundMap::SetUniversalGround().
| void Isis::Projection::SetUpperLeftCorner | ( | const Displacement & | x, |
| const Displacement & | y ) |
This method searches for extreme (min/max/discontinuity) coordinate values along the constBorder line between minBorder and maxBorder (that is, across latitudes/longitudes).
This method locates the extrema by utilizing the findExtreme() method until the coordinate values converge. Then, extremeVal parameter is updated with this value before returning.
Discontinuities are stored in m_specialLatCases and m_specialLonCases so they may be checked again later, which creates significantly more accuracy in some cases.
| minBorder | Minimum latitude or longitude to search between. |
| maxBorder | Maximum latitude or longitude to search between. |
| extremeVal | The resulting global coordinate value (min or max value for x or y, depending on findMin and searchX) on the constBorder. |
| constBorder | The latitude or longitude that remains constant. The method will step along this border. |
| searchX | Indicates whether the method is searching for a min or max x-coordinate. If false the method searches for min or max y-coordinate. |
| searchLongitude | Indicates whether the method will search along a longitude. If true, constBorder is longitude and all other borders are latitudes. If false, the method searches a latitude (constBorder is a lat, other borders lons). |
| findMin | Indicates whether the method is looking for a minimum coordinate value. If false, the method is looking for a maximum value. |
This method looks for these extrema along the constBorder between minBorder and maxBorder by stepping along constBorder (10 times) from the minBorder and maxBorder. Then, the range of this extreme value is recorded in minBorder and maxBorder and the coordinate values corresponding to these new borders are stored in minBorderX, minBorderY, maxBorderX and maxBorderY.
This function should be used by calling it repeatedly until minBorderX and minBorderY do not equal maxBorderX and maxBorderY, respectively. Discontinuities will cause the minBorderX, minBorderY, maxBorderX and maxBorderY to never converge. If minBorderX never comes close to maxBorderX or minBorderY never comes close to maxBorderY, then between minBorder and maxBorder is the value of the most extreme value. In this case, either the smaller or larger of the x or y values found will be correct, depending on the values of findMin and searchX.
| minBorder | Minimum latitude or longitude to search between. This value gets updated to a more precise range. |
| maxBorder | Maximum latitude or longitude to search between. This value gets updated to a more precise range. |
| minBorderX | The x-value corresponding to the lower resultant minBorder and the constBorder, which is more accurate when nearly equal to maxBorderX. |
| minBorderY | The y-value corresponding to the lower resultant minBorder and the constBorder, which is more accurate when nearly equal to maxBorderY. |
| maxBorderX | The x-value corresponding to the higher resultant maxBorder and the constBorder, which is more accurate when nearly equal to minBorderX. |
| maxBorderY | The y-value corresponding to the higher resultant maxBorder and the constBorder, which is more accurate when nearly equal to minBorderY. |
| constBorder | The latitude or longitude that remains constant. The method will step along this border. |
| searchX | Indicates whether the method is searching for a min or max x-coordinate. If false the method searches for min or max y-coordinate. |
| searchLongitude | Indicates whether the method will search along a longitude. If true, constBorder is longitude and all other borders are latitudes. If false, the method searches a latitude (constBorder is a lat, other borders lons). |
| findMin | Indicates whether the method is looking for a minimum coordinate value. If false, the method is looking for a maximum value. |
This method is used by doSearch and findExtreme in order to set the ground correctly each time.
| variableBorder | The latitude or longitude that is variable in the search methods. |
| constBorder | The latitude or longitude that is constant in the search methods. |
| variableIsLat | Indicates whether variableBorder is the latittude value and constBorder is the longitude value. If false, variableBorder is the longitude value and constBorder is the latitude value. |
| x | the upper left corner x value |
| y | the upper left corner y value |
References Isis::PvlContainer::addKeyword(), m_mappingGrp, Isis::Displacement::meters(), Isis::PvlContainer::Replace, and Isis::toString().
|
virtual |
This method is used to set a world coordinate.
A world coordinate is a different coordinate type that has a one-to-one mapping to the projection coordinate system. For example, mapping pixel samples and lines to projection x's and y's. The Set forces an attempted calculation of the corresponding latitude/longitude position. This may or may not be successful and a status is returned as such. Note that is only applies if the Projection object was given an WorldMapper object during construction. If an WorldMapper was not supplied then SetWorld operates exactly the same as SetCoordinate (impling that world coordinate and projection coordinate are identical).
| worldX | World X coordinate in units that are specified by the WorldMapper object (e.g., pixels, millimeters, etc) |
| worldY | World Y coordinate in units that are specified by the WorldMapper object (e.g., pixels, millimeters, etc) |
References m_mapper, Isis::WorldMapper::ProjectionX(), Isis::WorldMapper::ProjectionY(), and SetCoordinate().
Referenced by Isis::ProcessExport::CreateWorldFile(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::SetImage(), Isis::SubArea::UpdateLabel(), and Isis::PolygonTools::XYToLatLon().
| void Isis::Projection::SetWorldMapper | ( | WorldMapper * | mapper | ) |
If desired the programmer can use this method to set a world mapper to be used in the SetWorld, WorldX, and WorldY methods.
Mappers typically transform a projection coordinate (x/y) into the desired working coordinate system, for example, cube pixels or inches on a piece of paper. They transform in both directions (world to projection and projection to world). This allows for conversions from line/sample to latitude/longitude and vice versa. This projection will take ownership of the WorldMapper pointer.
| mapper | Pointer to the mapper |
References m_mapper.
|
protected |
This protected method is a helper for derived classes.
It takes a rotated x,y and stores them in the current x and y data members.
| x | The rotated x coordinate. |
| y | The rotated y coordinate. |
References m_good, and Isis::Null.
Referenced by Isis::Equirectangular::SetCoordinate(), Isis::LambertConformal::SetCoordinate(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Mercator::SetCoordinate(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Orthographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Planar::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PointPerspective::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PolarStereographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::RingCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Robinson::SetCoordinate(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Sinusoidal::SetCoordinate(), Isis::TProjection::SetCoordinate(), and Isis::TransverseMercator::SetCoordinate().
|
static |
Converts the given angle (in degrees) to degrees, minutes, seconds.
Outputs in the form xxx yym zz.zzzs, for example, 206.291 degrees is 206 17m 27.6s
| angle | Angle in degrees to be converted to degrees, minutes, seconds |
|
static |
|
static |
| double Isis::Projection::ToProjectionX | ( | const double | worldX | ) | const |
This method converts a world x value to a projection x value.
For example, if the world coordinate system is an image then this method converts a sample position to a projection x value. Note that if SetWorldMapper is not used then this routine simply returns the value of the argument. That is, no mapping occurs.
| worldX | World x coordinate |
| IException::Unknown | - "The given x-value is invalid." |
References _FILEINFO_, m_mapper, Isis::Null, Isis::WorldMapper::ProjectionX(), and Isis::IException::Unknown.
| double Isis::Projection::ToProjectionY | ( | const double | worldY | ) | const |
This method converts a world y value to a projection y value.
For example, if the world coordinate system is an image then this method converts a line position to a projection y value. Note that if SetWorldMapper is not used then this routine simply returns the value of the argument. That is, no mapping occurs.
| worldY | World y coordinate |
| IException::Unknown | - "The given y-value is invalid." |
References _FILEINFO_, m_mapper, Isis::Null, Isis::WorldMapper::ProjectionY(), and Isis::IException::Unknown.
| double Isis::Projection::ToWorldX | ( | const double | projectionX | ) | const |
This method converts a projection x value to a world x value.
For example, if the world coordinate system is an image then this method converts a projection x to a sample position. Note that if SetWorldMapper is not used then this routine simply returns the value of the argument. That is, no mapping occurs.
| projectionX | Projection x value in meters |
| IException::Unknown | - "The given x-value is invalid." |
References _FILEINFO_, m_mapper, Isis::Null, Isis::IException::Unknown, and Isis::WorldMapper::WorldX().
| double Isis::Projection::ToWorldY | ( | const double | projectionY | ) | const |
This method converts a projection y value to a world y value.
For example, if the world coordinate system is an image then this method converts a projection y to a line position. Note that if SetWorldMapper is not used then this routine simply returns the value of the argument. That is, no mapping occurs.
| projectionY | Projection y value in meters |
| IException::Unknown | - "The given y-value is invalid." |
References _FILEINFO_, m_mapper, Isis::Null, Isis::IException::Unknown, and Isis::WorldMapper::WorldY().
|
pure virtual |
This method returns the Version of the map projection.
It is a pure virtual method (requires all subclasses to override).
Implemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::Planar, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TransverseMercator, Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal, Isis::RingPlaneProjection, and Isis::TProjection.
|
virtual |
This returns the world X coordinate provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success.
Success can also be checked using the IsGood method. The units of X will be in the units as specified by the WorldMapper object which was given to the SetWorldMapper method. If a mapper object was not given then world coordinates are the same as the projection coordinates (i.e., WorldX and XCoord will return the same value).
References m_mapper, and Isis::WorldMapper::WorldX().
Referenced by Isis::DemShape::localRadius(), Isis::UniversalGroundMap::Sample(), and Isis::Camera::SetRightAscensionDeclination().
|
virtual |
This returns the world Y coordinate provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success.
Success can also be checked using the IsGood method. The units of Y will be in the units as specified by the WorldMapper object which was given to the SetWorldMapper. If a mapper object was not given then world coordinates are the same as the projection coordinates (i.e., WorldY and YCoord will return the same value).
References m_mapper, and Isis::WorldMapper::WorldY().
Referenced by Isis::UniversalGroundMap::Line(), Isis::DemShape::localRadius(), and Isis::Camera::SetRightAscensionDeclination().
| double Isis::Projection::XCoord | ( | ) | const |
This returns the projection X provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success.
Success can also be checked using the IsGood method. The units of X will be in the same . units as the radii obtained from the label.
Referenced by Isis::MosaicFindTool::getUserGroundPoint(), Isis::PolygonTools::LatLonToXY(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::TProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::MosaicAreaTool::userChangedBox(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::PointPerspective::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck().
|
pure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::Equirectangular, Isis::LambertAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::LambertConformal, Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea, Isis::Mercator, Isis::Mollweide, Isis::ObliqueCylindrical, Isis::Orthographic, Isis::Planar, Isis::PointPerspective, Isis::PolarStereographic, Isis::RingCylindrical, Isis::RingPlaneProjection, Isis::Robinson, Isis::SimpleCylindrical, Isis::Sinusoidal, Isis::TProjection, Isis::TransverseMercator, and Isis::UpturnedEllipsoidTransverseAzimuthal.
|
protectedpure virtual |
Implemented in Isis::TProjection, and Isis::RingPlaneProjection.
| double Isis::Projection::YCoord | ( | ) | const |
This returns the projection Y provided SetGround, SetCoordinate, SetUniversalGround, or SetWorld returned with success.
Success can also be checked using the IsGood method. The units of Y will be in the same units as the radii obtained from the label.
Referenced by Isis::MosaicFindTool::getUserGroundPoint(), Isis::PolygonTools::LatLonToXY(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::TProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::MosaicAreaTool::userChangedBox(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::PointPerspective::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck().
|
protected |
Indicates if the contents of m_x, m_y, m_latitude, and m_longitude are valid.
Referenced by IsGood(), Projection(), SetComputedXY(), Isis::Equirectangular::SetCoordinate(), Isis::LambertConformal::SetCoordinate(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Mercator::SetCoordinate(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Orthographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Planar::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PointPerspective::SetCoordinate(), Isis::PolarStereographic::SetCoordinate(), Isis::RingCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Robinson::SetCoordinate(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Sinusoidal::SetCoordinate(), Isis::TProjection::SetCoordinate(), Isis::TransverseMercator::SetCoordinate(), Isis::Equirectangular::SetGround(), Isis::LambertConformal::SetGround(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::SetGround(), Isis::Mercator::SetGround(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::SetGround(), Isis::Orthographic::SetGround(), Isis::PointPerspective::SetGround(), Isis::PolarStereographic::SetGround(), Isis::Robinson::SetGround(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::SetGround(), Isis::Sinusoidal::SetGround(), Isis::TProjection::SetGround(), Isis::TransverseMercator::SetGround(), Isis::Planar::SetGround(), Isis::RingCylindrical::SetGround(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetGround(), SetUnboundUniversalGround(), Isis::TProjection::SetUnboundUniversalGround(), SetUniversalGround(), Isis::TProjection::SetUniversalGround(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::SetUniversalGround(), SetXY(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck().
|
protected |
Indicates if the ground range (min/max lat/lons) were read from the labels.
Referenced by HasGroundRange(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::RingPlaneProjection(), Isis::TProjection::TProjection(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRange(), and Isis::TProjection::XYRange().
|
protected |
This points to a mapper passed into the SetWorldMapper method.
This mapper allows the programmer to specify a different world coordinate system. Thus the programmer could pass in line/sample positions in order to obtain a latitude/longitude or set a lat/lon and get a line/sample.
Referenced by Projection(), Resolution(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::Scale(), Isis::TProjection::Scale(), SetWorld(), SetWorldMapper(), ToProjectionX(), ToProjectionY(), ToWorldX(), ToWorldY(), WorldX(), WorldY(), and ~Projection().
|
protected |
Mapping group that created this projection.
Referenced by Isis::Equirectangular::Mapping(), Isis::LambertConformal::Mapping(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::Mapping(), Isis::Mercator::Mapping(), Isis::ObliqueCylindrical::Mapping(), Isis::Orthographic::Mapping(), Isis::PointPerspective::Mapping(), Isis::PolarStereographic::Mapping(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::Mapping(), Isis::Robinson::Mapping(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::Mapping(), Isis::Sinusoidal::Mapping(), Isis::TProjection::Mapping(), Isis::TransverseMercator::Mapping(), Isis::Equirectangular::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::LambertConformal::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::Mercator::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::Orthographic::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::PointPerspective::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::PolarStereographic::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::TProjection::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::TransverseMercator::MappingLatitudes(), Isis::Equirectangular::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::LambertConformal::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::Mercator::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::Orthographic::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::PointPerspective::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::PolarStereographic::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::Robinson::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::Sinusoidal::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::TProjection::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::TransverseMercator::MappingLongitudes(), Isis::Planar::MappingRingLongitudes(), Isis::RingCylindrical::MappingRingLongitudes(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::MappingRingLongitudes(), Isis::Planar::MappingRingRadii(), Isis::RingCylindrical::MappingRingRadii(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::MappingRingRadii(), Projection(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::RingPlaneProjection(), SetUpperLeftCorner(), and Isis::TProjection::TProjection().
|
protected |
See minimumX description.
Referenced by Projection(), Isis::Equirectangular::XYRange(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::XYRange(), Isis::Mercator::XYRange(), Isis::Orthographic::XYRange(), Isis::Planar::XYRange(), Isis::PolarStereographic::XYRange(), Isis::RingCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Robinson::XYRange(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Sinusoidal::XYRange(), Isis::TransverseMercator::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::TProjection::xyRangeOblique().
|
protected |
See minimumX description.
Referenced by Projection(), Isis::Equirectangular::XYRange(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::XYRange(), Isis::Mercator::XYRange(), Isis::Orthographic::XYRange(), Isis::Planar::XYRange(), Isis::PolarStereographic::XYRange(), Isis::RingCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Robinson::XYRange(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Sinusoidal::XYRange(), Isis::TransverseMercator::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::TProjection::xyRangeOblique().
|
protected |
The data elements m_minimumX, m_minimumY, m_maximumX, and m_maximumY are convience data elements when you write the XYRange virtual function.
They are used in conjuction with the XYRangeCheck convience method. After utilizing XYRangeCheck to test boundary conditions in the XYRange method these values will contain the projection x/y coverage for the ground range specified by min/max lat/lon.
Referenced by Projection(), Isis::Equirectangular::XYRange(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::XYRange(), Isis::Mercator::XYRange(), Isis::Orthographic::XYRange(), Isis::Planar::XYRange(), Isis::PolarStereographic::XYRange(), Isis::RingCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Robinson::XYRange(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Sinusoidal::XYRange(), Isis::TransverseMercator::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::TProjection::xyRangeOblique().
|
protected |
See minimumX description.
Referenced by Projection(), Isis::Equirectangular::XYRange(), Isis::LambertConformal::XYRange(), Isis::LunarAzimuthalEqualArea::XYRange(), Isis::Mercator::XYRange(), Isis::Orthographic::XYRange(), Isis::Planar::XYRange(), Isis::PolarStereographic::XYRange(), Isis::RingCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Robinson::XYRange(), Isis::SimpleCylindrical::XYRange(), Isis::Sinusoidal::XYRange(), Isis::TransverseMercator::XYRange(), Isis::TProjection::XYRangeCheck(), Isis::RingPlaneProjection::XYRangeCheck(), and Isis::TProjection::xyRangeOblique().
|
protected |
Indicates whether projection is sky or land.
Referenced by IsSky(), and Projection().