ISIS Application Documentation
jigsaw | Standard View | TOC | Home |
Improves camera pointing and a whole lot more!
Description
Categories
Groups
Examples
History
Things To Do
Description
The jigsaw application performs a bundle adjustment on a group of overlapping Isis, level 1, cubes from framing and/or line-scan cameras. The adjustment simultaneously defines the selected image geometry information (camera pointing, spacecraft position) and control point coordinates (x,y,z or lat,lon,radius) to reduce boundary mismatches in mosaics of the images.
This functionality is demonstrated below in a zoomed-in area of a mosaic of a pair of overlapping Messenger images. In the before jigsaw mosaic on the left (uncontrolled), the features on the edges of the images do not match. In the after jigsaw mosaic on the right (controlled), the crater edges meet correctly and the seam between the two images is no longer visible.


The jigsaw application assumes spiceinit has been run on the input cubes so that SPICE is included in the Isis cube labels in the Kernels group. In order to run the program, the user must provide a list of input cubes, an input control net, the name of an output control net, and the adjustment parameters. jigsaw outputs a new control net that includes the initial state of the points in the network and their final state after the adjustment. The initial states of the points are tagged as a priori in the control net, and their final states are tagged as adjusted. The measured sample/line positions associated with the control points in the net are not changed. SPICE in the cube labels is updated at the end of the adjustment only if the bundle converges and the UPDATE parameter is selected.
Optional output files can be selected to provide more information for analyzing the results. BUNDLEOUT_TXT provides an overall summary of the bundle adjustment. It lists the user input parameters selected and tables of statistics for both the images and the points. The image statistics can also be written to a separate CSV file and likewise for the point statistics with the OUTPUT_CSV option selected. RESIDUALS_CSV provides a table of the measured image coordinates and the final sample, line, and overall residuals in both millimeters and pixels.
The functional model for the bundle adjustment is the collinearity condition. It stipulates that the camera perspective center, a ground point, and its associated image point measurement be collinear. The diagram below demonstrates the collinear condition in a bundle adjustment. The vectors formed by connecting each object space point (target surface x,y,z) and its corresponding image space points (sample,line) form a bundle of light rays.
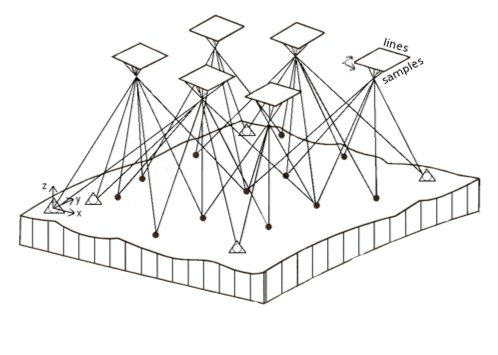
Kraus, Karl., 1993. Photogrammetry Vol. I., Fundamentals and Standard Processes, Der. Dümmler Verlag, Bonn, Germany, ISBN 3-427-78684-6, 397 pages.
Relevant Documentation
For information on what the original jigsaw code was based on checkout Rand Notebook
Known Issues
Running jigsaw with a control net containing JigsawRejected flags may result in bundle failureWhen running jigsaw with Outlier Rejection turned on, control points and/or control measures may be flagged as JigsawRejected in the output control net file. If this output net file is then used in a subsequent jigsaw run, these points and measures will be erroneously ignored, potentially causing the bundle adjustment to fail.
--Workarounds
- Run jigsaw with Outlier Rejection off.
- Do not use the output control net file in subsequent jigsaw runs.
- Convert the output control net file from binary to PVL and back using cnetbin2pvl and cnetpvl2bin. This will clear the JigsawRejected flags.
Solving for the target body radii (triaxial or mean) is NOT possible and likely increases error in the solve.With the current jigsaw implementation, it is NOT possible to individually solve for either the mean or triaxial radii as seperate calculations in the bundle adjustment. More specifically, the target body radii has no effect when solving for individual points and thus cannot be solved for in the bundle. A local radii solve is already part of the sequence of equations that jigsaw uses to compute various partial derivatives to populate the solve matrix. A seperate mean or triaxial radii solve can be applied to the target body and the partials from this separate application are added to the solve matrix. This option adds additional computation time to jigsaw and creates additional uncertainty/error in the bundle adjust. We advise the mean and triaxial radii solve be avoided.
If you are trying to generate a spheroid from a control network there are other programs that can do this for you. An easier but more naive method is ingesting the OUTPUT_CSV from your network, gather local radii information from those points, then generate a sphereiod from those local radii.
Categories
Related Objects and Documents
Applications
Parameter Groups
Files
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FROMLIST | List of cubes in the input control network |
| HELDLIST | List of (non-overlapping) cubes to hold in the adjustment |
| CNET | Input control network |
| ONET | Output control network |
| SCCONFIG | File containing Camera/Spacecraft parameters |
Solve Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| OBSERVATIONS | Keep instances of the same observation in different cube files the same |
| RADIUS | Solve for local radii of points |
| UPDATE | Update cube label |
| OUTLIER_REJECTION | Auto-rejection of outliers |
| REJECTION_MULTIPLIER | Rejection multiplier |
| ERRORPROPAGATION | Compute variance-covariance matrix |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MODEL1 | A maximum likelihood estimation model selection |
| MAX_MODEL1_C_QUANTILE | Quantile of the |residual| distribution used to set the tweaking constant of the maximum likelihood estimation model |
| MODEL2 | A maximum likelihood estimation model selection |
| MAX_MODEL2_C_QUANTILE | Quantile of the |residual| distribution used to set the tweaking constant of the maximum likelihood estimation model |
| MODEL3 | A maximum likelihood estimation model selection |
| MAX_MODEL3_C_QUANTILE | Quantile of the |residual| distribution used to set the tweaking constant of the maximum likelihood estimation model |
Convergence Criteria
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SIGMA0 | Standard deviation of unit weight |
| MAXITS | Maximum number of iterations |
Camera Pointing Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CKDEGREE | Degree of polynomial fit to original camera angles |
| CKSOLVEDEGREE | The degree of the polynomial being fit to in the bundle adjustment |
| CAMSOLVE | Camera pointing parameters to include in the bundle adjustment |
| TWIST | Solve for twist |
| OVEREXISTING | Fit polynomial over the existing pointing |
Spacecraft Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SPKDEGREE | Degree of polynomial fit to original camera position |
| SPKSOLVEDEGREE | The degree of the camera position polynomial being fit to in the bundle adjustment. |
| SPSOLVE | Spacecraft position parameters to include in the adjustment |
| OVERHERMITE | Fit polynomial over the existing Hermite spline |
Community Sensor Model Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CSMSOLVESET | Specify a set of a CSM parameters to solve for. |
| CSMSOLVETYPE | Specify a type of a CSM parameters to solve for. |
| CSMSOLVELIST | Specify an explicit list of CSM parameters to solve for. |
Target Body
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SOLVETARGETBODY | Solve for target body parameters. The parameters, their a priori values, and uncertainties are input using a PVL file specified by TBPARAMETERS below. |
| TBPARAMETERS | File containing target body parameters to solve for, their a priori values and uncertainties. |
Control Point Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| CONTROL_POINT_COORDINATE_TYPE_BUNDLE | Coordinate type to use for bundling and outputting control points |
| CONTROL_POINT_COORDINATE_TYPE_REPORTS | Coordinate type to use for bundling and outputting control points |
Parameter Uncertainties
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| POINT_LATITUDE_SIGMA | Global latitude uncertainty for all points (meters) |
| POINT_LONGITUDE_SIGMA | Global longitude uncertainty for all points (meters) |
| POINT_RADIUS_SIGMA | Global radius uncertainty for all points (meters) |
| POINT_X_SIGMA | Global body-fixed X uncertainty for all points (meters) |
| POINT_Y_SIGMA | Global body-fixed X uncertainty for all points (meters) |
| POINT_Z_SIGMA | Global body-fixed X uncertainty for all points (meters) |
| SPACECRAFT_POSITION_SIGMA | Global uncertainty for spacecraft coordinates (meters) |
| SPACECRAFT_VELOCITY_SIGMA | Global uncertainty for spacecraft velocity (meters/second) |
| SPACECRAFT_ACCELERATION_SIGMA | Global uncertainty for spacecraft acceleration (meters/second/second) |
| CAMERA_ANGLES_SIGMA | global uncertainty for camera angles (decimal degrees) |
| CAMERA_ANGULAR_VELOCITY_SIGMA | Global uncertainty for camera angular velocity (decimal degrees/second) |
| CAMERA_ANGULAR_ACCELERATION_SIGMA | Global uncertainty for camera angular acceleration (decimal degrees/second/second) |
Output Options
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FILE_PREFIX | Output file prefix |
| BUNDLEOUT_TXT | Standard bundle output file - bundleout.txt |
| IMAGESCSV | Outputs image data (body-fixed) to csv file - bundleout_images.csv |
| OUTPUT_CSV | Outputs point and image data (body-fixed) to csv file - bundleout_points.csv |
| RESIDUALS_CSV | Outputs image coordinate residuals to csv file - residuals.csv |
Files: FROMLIST
Description
This file contains a list of all cubes in the control network
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Filter | *.txt *.lis |
Files: HELDLIST
Description
This file contains a list of all cubes whose orientation and position will be held in the adjustment. These images will still be included in the solution, but their camera orientation and spacecraft position will be constrained to keep the values from changing. This is an optional parameter and the default is to not hold any of the images. Note that held images must not overlap each other to work properly.
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Internal Default | none |
| Filter | *.txt *.lis |
Files: CNET
Description
This file is a control network generated from programs such as autoseed or qnet. It contains the control points and associated measures.
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Filter | *.net |
Files: ONET
Description
This output file contains the updated control network with the final coordinates of the control points and residuals for each measurement.
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | output |
| Filter | *.net |
Files: SCCONFIG
Description
This file contains the Camera/Spacecraft parameters to use when processing images from different sensors. This file should be in PVL format. It should contain an object called SensorParameters with one group per spacecraft/instrument combination. The SpacecraftName and InstrumentId keywords in the Instrument group of an image file are used to create the name of each group in the PVL file. The group pertaining to each spacecraft/instrument should contain the keyword/value pairs needed to process images taken with that sensor: CKDEGREE, CKSOLVEDEGREE, CAMSOLVE, TWIST, OVEREXISTING, SPKDEGREE, SPKSOLVEDEGREE, SPSOLVE, OVERHERMITE, SPACECRAFT_POSITION_SIGMA, SPACECRAFT_VELOCITY_SIGMA, SPACECRAFT_ACCELERATION_SIGMA, CAMERA_ANGLES_SIGMA, CAMERA_ANGULAR_VELOCITY_SIGMA, CAMERA_ANGULAR_ACCELERATION_SIGMA. If any of these keywords are missing, then their defaults will be used. There is an example template at $ISISROOT/appdata/templates/jigsaw/SensorParameters.pvl that can be used as a guide.
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Exclusions |
|
| Filter | *.pvl |
Solve Options: OBSERVATIONS
Description
This option will solve for SPICE on all cubes with a matching observation number as though they were a single observation. For most missions, the default observation number is equivalent to the serial number of the cube, and a single cube is an observation. However, for the Lunar Orbiter mission, an image has a defined observation number that is a substring of its serial number. This feature allows the three subframes of a Lunar Orbiter High Resolution frame to be treated as a single observation when this option is used; otherwise, each subframe is adjusted independently.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
Solve Options: RADIUS
Description
Select this option to solve for the local radius of each control point. If this button is not turned on, the radii of the points will not change from the cube's shape model.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
| Inclusions |
|
Solve Options: UPDATE
Description
When this option is selected, the application will update the labels of the individual cubes in the FROMLIST with the final values from the solution if the adjustment converges. The results are written to the SPICE blobs attached to the cube, overwriting the previous values. If this option is not selected, the cube files are not changed. All other output files are still created.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
Solve Options: OUTLIER_REJECTION
Description
Select this option to perform automatic outlier detection and rejection.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
| Exclusions |
|
| Inclusions |
|
Solve Options: REJECTION_MULTIPLIER
Description
Rejection multiplier
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Default | 3.0 |
| Inclusions |
|
Solve Options: ERRORPROPAGATION
Description
Select this option to compute the variance-covariance matrix of the parameters. The parameter uncertainties can be computed from this matrix.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation: MODEL1
Description
A maximum likelihood estimation model selection.
| Type | string | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | NONE | ||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Maximum Likelihood Estimation: MAX_MODEL1_C_QUANTILE
Description
The tweaking constant has different meanings depending on the model being used: Huber models: The point at which the transformation motion from L2 to L1 norms takes place. Recommended quantile: 0.5 Welsch model: Residuals whose absolute value is twice the tweaking constant are approaching negligible significance. Recommended quantile: 0.7 Chen model: Residuals whose absolute value is greater than the tweaking constant are totally ignored. Recommended quantile: > 0.9
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Default | 0.5 |
| Minimum | 0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1 (exclusive) |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation: MODEL2
Description
A maximum likelihood estimation model selection.
| Type | string | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | NONE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Maximum Likelihood Estimation: MAX_MODEL2_C_QUANTILE
Description
The tweaking constant has different meanings depending on the model being used: Huber models: The point at which the transformation motion from L2 to L1 norms takes place. Recommended quantile: 0.5 Welsch model: Residuals whose absolute value is twice the tweaking constant are approaching negligible significance. Recommended quantile: 0.7 Chen model: Residuals whose absolute value is greater than the tweaking constant are totally ignored. Recommended quantile: > 0.9
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Default | 0.5 |
| Minimum | 0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1 (exclusive) |
Maximum Likelihood Estimation: MODEL3
Description
A maximum likelihood estimation model selection.
| Type | string | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | NONE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Maximum Likelihood Estimation: MAX_MODEL3_C_QUANTILE
Description
The tweaking constant has different meanings depending on the model being used: Huber models: The point at which the transformation motion from L2 to L1 norms takes place. Recommended quantile: 0.5 Welsch model: Residuals whose absolute value is twice the tweaking constant are approaching negligible significance. Recommended quantile: 0.7 Chen model: Residuals whose absolute value is greater than the tweaking constant are totally ignored. Recommended quantile: > 0.9
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Default | 0.5 |
| Minimum | 0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1 (exclusive) |
Convergence Criteria: SIGMA0
Description
Converges on stabilization of Sigma0. Convergence occurs when the change in sigma0 between iterations is less than or equal to Sigma0.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Default | 1.0e-10 |
| Minimum | 0 (exclusive) |
Convergence Criteria: MAXITS
Description
Maximum number of times to iterate. The application stops iterating at MAXIT, or when convergence is reached.
| Type | integer |
|---|---|
| Default | 50 |
| Minimum | 1 (inclusive) |
Camera Pointing Options: CKDEGREE
Description
The degree of the polynomial fit to the original camera angles and used to generate a priori camera angles for the first iteration.
| Type | integer |
|---|---|
| Default | 2 |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Camera Pointing Options: CKSOLVEDEGREE
Description
The degree of the polynomial being fit to in the bundle adjust solution. This polynomial can be different from the one used to generate the a priori camera angles used in the first iteration. In the case of an instrument with a jitter problem, a higher degree polynomial fit to each of the camera angles might provide a better solution (smaller errors). For framing cameras, the application automatically sets degree to 0.
| Type | integer |
|---|---|
| Default | 2 |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Camera Pointing Options: CAMSOLVE
Description
This parameter is used to specify which, if any, camera pointing parameters to include in the adjustment.
| Type | string | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | ANGLES | ||||||||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Camera Pointing Options: TWIST
Description
If this option is selected, the twist angle will be adjusted in the bundle adjustment solution.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | Yes |
Camera Pointing Options: OVEREXISTING
Description
This option will fit a polynomial over the existing pointing data. This data is held constant in the adjustment, and the initial value for the each of the coefficients in the polynomials is 0. When this option is used, the current pointing is used as a priori in the adjustment.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
Spacecraft Options: SPKDEGREE
Description
The degree of the polynomial fit to the original camera position and used to generate a priori camera positions for the first iteration.
| Type | integer |
|---|---|
| Default | 2 |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Spacecraft Options: SPKSOLVEDEGREE
Description
The degree of the polynomial being fit to in the bundle adjust solution. This polynomial can be different from the one used to generate the a priori camera positions used in the first iteration. In the case of an instrument with a jitter problem, a higher degree polynomial fit for the camera position might provide a better solution (smaller errors). For framing cameras, the application automatically sets degree to 0.
| Type | integer |
|---|---|
| Default | 2 |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Spacecraft Options: SPSOLVE
Description
This parameter is used to specify which, if any, spacecraft position parameters to include in the adjustment.
| Type | string | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | NONE | ||||||||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Spacecraft Options: OVERHERMITE
Description
This option will fit a polynomial over the existing Hermite cubic spline used to interpolate the coordinates of the spacecraft position. The spline is held constant in the adjustment, and the initial value for the each of the coefficients in the polynomials is 0. When this option is used, the current positions are used as a priori in the adjustment.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | No |
Community Sensor Model Options: CSMSOLVESET
Description
Specify one of the parameter sets from the CSM GeometricModel API to solve for. All parameters belonging to the specified set will be solved for.
| Type | string | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Internal Default | none | ||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
||||||||||||
| Exclusions |
|
Community Sensor Model Options: CSMSOLVETYPE
Description
Specify a parameter type from the CSM GeometricModel API to solve for. All parameters of the specified type will be solved for.
| Type | string | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Option List: |
|
|||||||||||||||
| Exclusions |
|
Community Sensor Model Options: CSMSOLVELIST
Description
All CSM parameters in this list will be solved for. Trailing and leading whitespace will be stripped off. Use standard ISIS parameter array notation to specify multiple parameters.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Exclusions |
|
Target Body: SOLVETARGETBODY
Description
Solve for target body parameters. The parameters, their a priori values, and uncertainties are input using a PVL file specified by TBPARAMETERS below. An example template PVL file is located at $ISISROOT/appdata/templates/jigsaw/TargetBodyParameters.pvl.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | false |
| Inclusions |
|
Target Body: TBPARAMETERS
Description
This file contains target body parameters to solve for in the bundle adjustment, their a priori values, and uncertainties. The file must be in PVL format. An example template PVL file is located at $ISISROOT/appdata/templates/jigsaw/TargetBodyParameters.pvl. Instructions for the PVL structure are given in the template.
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Filter | *.pvl |
Control Point Parameters: CONTROL_POINT_COORDINATE_TYPE_BUNDLE
Description
This parameter indicates which coordinate type will be used to present the control points in the bundle adjustment and bundle output.
| Type | string | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | LATITUDINAL | |||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Control Point Parameters: CONTROL_POINT_COORDINATE_TYPE_REPORTS
Description
This parameter indicates which coordinate type will be used to present the control points in the bundle adjustment and bundle output.
| Type | string | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | LATITUDINAL | |||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Parameter Uncertainties: POINT_LATITUDE_SIGMA
Description
This optional value will be used as the global latitude uncertainty for all points. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: POINT_LONGITUDE_SIGMA
Description
This optional value will be used as the global longitude uncertainty for all points. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: POINT_RADIUS_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global radius uncertainty for all points. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
| Inclusions |
|
Parameter Uncertainties: POINT_X_SIGMA
Description
This optional value will be used as the global uncertainty for all points. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: POINT_Y_SIGMA
Description
This optional value will be used as the global uncertainty for all points. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: POINT_Z_SIGMA
Description
This optional value will be used as the global uncertainty for all points. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: SPACECRAFT_POSITION_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global uncertainty for spacecraft coordinates. Units are meters.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: SPACECRAFT_VELOCITY_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global uncertainty for spacecraft velocity. Units are meters/second.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: SPACECRAFT_ACCELERATION_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global uncertainty for spacecraft acceleration. Units are meters/second/second.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: CAMERA_ANGLES_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global uncertainty for camera angles. Units are decimal degrees.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: CAMERA_ANGULAR_VELOCITY_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global uncertainty for camera angular velocity. Units are decimal degrees/second.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Parameter Uncertainties: CAMERA_ANGULAR_ACCELERATION_SIGMA
Description
This value will be used as the global uncertainty for camera angular acceleration. Units are decimal degrees/second/second.
| Type | double |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
| Minimum | 0 (inclusive) |
Output Options: FILE_PREFIX
Description
File prefix to prepend for the generated output files. Any prefix that is not a file path will have an underscore placed between the prefix and file name.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Internal Default | none |
Output Options: BUNDLEOUT_TXT
Description
Selection of this parameter flags generation of the standard bundle output file
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | yes |
Output Options: IMAGESCSV
Description
Selection of this parameter flags output of image data (in body-fixed coordinates) to a csv file.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | yes |
Output Options: OUTPUT_CSV
Description
Selection of this parameter flags output of point and image data (in body-fixed coordinates) to csv file.
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | yes |
Output Options: RESIDUALS_CSV
Description
Selection of this parameter flags output of image coordinate residuals to a csv file
| Type | boolean |
|---|---|
| Default | yes |
Examples
Example 1
Simple run of jigsaw with images from a linescanner
Description
This example runs jigsaw in a very simple way using four MRO CTX images. Only the required parameters are entered, with all other parameters left at their default settings. This bundle solution only solves for the camera orientation (see the CAMSOLVE and TWIST parameters). This command does not update the SPICE information attached to the four cubes.
A possible use for this simple run would be to test a network to identify control points that are not well placed.
Command Line
GUI Screenshot
|
jigsaw Linescan image example
|
Example GUI
The top of the GUI shows the parameters filled in for input cube list,
the input control network and the output control network. All other parameters
were left at their default values.
|
Data File
| Cube list file | Input file defining the file names of the four cubes used in the control network. The file names can include a path if needed. Each file name is on a separate line and the last file name can have new line at the end, but it is not required. |
|---|
Example 2
Run of jigsaw parameterized for Kaguya Terrain Camera (TC) images and a relative control network covering the Apollo 15 landing site.
Description
A relative network is a network that connects overlapping images with tie points but has no tie points connected to a ground source. Since there is no connection to ground in the network, this bundle will only solve for camera specific parameters. The bundle could still solve for other parameters and be correct relative to the camera position, but it would increase the complexity of the bundle. The proceeding two examples will include grounded networks, so we will wait to increase the complexity of the bundle until ground points are included. Additionally, in this example we are evaluating the solution and do not want to apply it to the images yet, therefore, update is set to ‘no’.
This relative bundle turns on and parameterizes the camera twist and camera acceleration solve parameters. Camera twist is a flag that allows the bundle to solve for the camera's rotation around the bore sight axis and uses the same uncertainty estimation as the other two rotations. Setting the camera solve parameter to acceleration, however, does require uncertainties to be set for the angles (deg), angular velocity (deg/s), and angular accelerations (deg/s**2). These values were set with increasing constraint because of the increasing affect alterations of higher order parameters have on the bundle solution.
The ‘overexisting’ flag tells the bundle solution to approximate the camera rotation with a zero polynomial function added to the existing rotation data (adding the polynomial over the existing data). Without the ‘overexisting’ flag, the bundle fits a polynomial to the existing rotations, throws out the existing data points, and uses the polynomial to calculate the approximate ephemerides when needed.
This bundle also lowers the max iterations to 10 (from default 50). Lowering the max iterations does not affect the bundle solution. However, setting a lower iteration limit can serve as a flag if you expect your network to bundle quickly. Finally, the sigma0 convergence criteria was not changed from its default value, it was only explicitly stated in this call.
Command Line
Example 3
Run of jigsaw parameterized for Kaguya Terrain Camera (TC) images and an intermediate ground control network covering the Apollo 15 landing site.
Description
This example jigsaw bundle is run directly after adding ground control points to the previous relative network. With ground control points inserted into the bundle solution, we will expand the bundle solve parameters to attempt solving for point radius values and the position of the spacecraft.
Ground points are weighted more heavily in the bundle than relative control points and adding parameters adds more complexity to the bundle solution. Therefore, it is common to create and refine a network with only relative points and add ground point in after the relative network (and its bundle solution) is of sufficient quality. The purpose of this bundle is to ensure the network bundle converges with the added ground points and solve parameters, before committing to updating the camera pointing on the images, so update is set to 'no'.
In addition to the previous solve parameters, this bundle turns on the point radius and spacecraft position solve parameters. Applying the point radius solve parameter requires the point_radius_sigma to be set. This value is a representation the uncertainty (in meters) of the cameras apriori pointing corresponding to the correct elevation on the shape model; this value is not a hard constraint. Often this value can be set, and the appropriateness of the set value can be checked using the 'POINTS DETAIL' section of the bundleout.txt file output by jigsaw. If more than half of the radius total corrections exceed the provided sigma, the uncertainty may need to be increased.
Applying the space craft position solve parameter requires an uncertainty estimation through spacecraft_position_sigma (again this value is not a hard constraint). The appropriateness of the provided sigma can be evaluated through the bundleout_images.csv X Correction, Y Correction, and Z Correction columns.
The 'overhermite' flag allows an estimation the spacecraft position like the 'overexisting' flag estimates the camera pointing, with a zero-polynomial added over the existing data (for spacecraft position this is a cubic Hermite spline). These options require more memory but provide a solution more representative of small variations in the original ephemeris data.
Command Line
Data File
| jig1rr_bundleout.txt | A shorten example of a typical bundleout.txt file produced by a jigsaw run with error propegation. This file was trimmed to hold 10 images, 50 relative points, and all ground points along with their associated detail sections. Bundleout files typically contain all image and point from a network put through jigsaw. |
|---|
Example 4
Run of jigsaw parameterized for Kaguya Terrain Camera (TC) images and a final ground control network covering Apollo 15 landing site.
Description
This last example is of a final jigsaw run of a grounded network. In this example all network adjustments are done, the bundle is converging, the resulting residuals are acceptable, and therefore we are ready to update the camera pointing on the cubes. During the final run we turn on the error propagation flag, this provides the variance-covariance matrix of the parameters, from which uncertainties can be computed. This is valuable if you plan to compute certainties for your update cubes camera pointing (or any kernels resulting from these updated camera pointings).
If you want to double check the update was completed, see cathist or catlab (search for ‘Jigged’).
Command Line
Data Files
| jig1rrEP_bundleout.txt | A shorten example of a typical bundleout.txt file produced by a jigsaw run with error propegation. This file was trimmed to hold 10 images, 50 relative points, and all ground points along with their associated detail sections. Bundleout files typically contain all image and point from a network put through jigsaw. |
|---|---|
| Instrument pointing and position tables before jigsaw update | Table summaries for the InstrumentPointing and InstrumentPosition tables extracted from a cube label. |
| Instrument point and position tables after jigsaw update | Table summaries for the InstrumentPointing and InstrumentPosition tables extracted from a jigsaw updated cube label. The InstrumentPointing table was updated due to the camera updates solved for in the bundle (camsolve=accelerations). The InstrumentPosition table was updated due to the spacecraft updates solved for in the bundle (spsolve=positions). |
History
| Jeff Anderson | 2007-04-27 | Original version |
| Steven Lambright | 2007-07-23 | Changed category to Control Networks and corrected XML bugs |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2007-10-05 | Revised iteration report to list the errors and sigmas from the same iteration. Previous version reported errors from previous iteration and sigmas from current iteration. |
| Christopher Austin | 2008-07-03 | Cleaned the Bundle Adjust memory leak and fixed the app tests. |
| Tracie Sucharski | 2009-04-08 | Added date to the Jigged comment in the spice tables. |
| Tracie Sucharski | 2009-04-22 | If updating pointing, delete the CameraStatistics table from labels. |
| Mackenzie Boyd | 2009-07-23 | Modified program to write history to input cubes. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2010-08-12 | Commented out Heldlist until mechanism in place to enter individual image parameter constraints. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2010-08-12 | Merged Ken Edmundson version with system and binary control net. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2011-06-14 | Modified code to prevent updates to cube files in held list. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2011-09-28 | Removed SC_SIGMAS from user parameter list because it is not fully implemented; changed method name SPARSE to OLDSPARSE and CHOLMOD to SPARSE; and improved the documentation for the Isis3.3.0 release. |
| Debbie A. Cook, Ken Edmundson, and Orrin Thomas | 2011-10-03 | Added images showing before and after to demonstrate the program. Added Krause's collinearity diagram and a brief explanation on the output options. Also added a lien for example(s) to be added later. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2011-10-06 | Corrected previous history entry and added references to glossary. Also changed application names to bold type. |
| Debbie A. Cook and Ken Edmundson | 2011-10-07 | Removed glossary references from briefs. Also changed the definition of angles to state right ascension and declination to be consistent with the output. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2011-10-14 | Added internal default and minimum inclusive tags to global apriori uncertainties. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2011-10-18 | Added Known Issues section and JigsawRejected flag issue. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2011-11-04 | Added minimums to parameters, corrected SOLVEDEGREE description, and added to the camsolve option descriptions in response to Mantis issue #514. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2011-12-20 | Added REJECTION_MULTIPLIER to interface, part of Mantis issue #637. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2012-01-19 | Added SPKDEGREE and SPKSOLVEDEGREE; changed name of SOLVEDEGREE to CKSOLVEDEGREE. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2014-02-13 | Added separate group for Error Propagation with option to write inverse matrix to binary file. For extremely large networks where memory/time for error propagation is limited. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2014-07-09 | Added USEPVL and SC_PARAMETERS parameters. |
| Jeannie Backer | 2014-07-14 | Modified appTests to use SPARSE method only. Commented out bundleout_images.csv references. Created observationSolveSettings() method to create an observation settings object from the user entered values. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2015-09-05 | Added preliminary target body functionality. Added SOLVETARGETBODY and TB_PARAMETERS. |
| Jesse Mapel | 2016-08-16 | Added a connection to allow jigsaw to surface exceptions from BundleAdjust. Fixes #2302 |
| Jeannie Backer | 2016-08-18 | Removed the user parameter called METHOD (i.e. the method used for solving the bundle matrix). This solve method is no longer user-selected. The program will now use what was called the SPARSE option for the METHOD parameter (i.e. solve with CholMod sparse decomposition). This method should give the same results as the other options and should run faster. So the other options were no longer needed. References #4162. |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-08-22 | Reviewed documentation and updated small spelling and grammar errors. References #4226. |
| Adam Paquette | 2016-08-31 | Updated how jigsaw handles its prefix parameter along with a small documentation change. Fixes #4309. |
| Jesse Mapel | 2016-09-02 | Updated how input parameters are output when using multiple sensor solve settings. Fixes #4316. |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-09-22 | Output from jigsaw will again provide "Validating network" and "Validation complete" messages to inform user that their control network has been validated. Fixes #4313. |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-10-05 | When running jigsaw with error propagation turned on, the correlation matrix file, inverseMatrix.dat, is no longer generated. Fixes #4315. |
| Tyler Wilson | 2016-10-06 | Added the IMAGES_CSV parameter to the "Output Options" group so that the user can now request the bundleout_images.csv file in addition to the other output files such as bundleout.txt. Fixes #4314. |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-10-13 | Implemented HELDLIST functionality for non-overlapping held images. Any control points that intersect the held images are fixed, and a priori surface points for these control points are set to the held images' measures' surface points. Disabled USEPVL/SC_PARAMETERS. Fixes #4293. |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-10-25 | Added the "Generating report files" and Rejected_Measures keyword back to jigsaw's standard output. Fixes #4461. Fixed spacing in standard output. Fixes #4462, #4463." |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-10-26 | The bundleout.txt output file will record default values for unsolved parameters. The default position will be the instrument position's center coordinate, and the default pointing will be the pointing's (rotation's) center angles. The bundleout_images.csv file will also have these defaults provided. Fixes #4464. |
| Makayla Shepherd | 2016-10-26 | Removed the underscores from the new parameters IMAGESCSV and TBPARAMETERS. |
| Ian Humphrey | 2016-11-16 | Exceptions that occur during the solving of the bundle adjustment will now pop up as message boxes when running jigsaw in GUI mode. Fixes #4483. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2016-11-17 | Output control net will be now be written regardless of whether bundle converges. Fixes #4533. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2017-01-17 | Updated description and brief for SOLVETARGETBODY and TBPARAMETERS. |
| Summer Stapleton | 2017-08-09 | Fixed bug where an invalid control net was not throwing exception. Fixes #5068. |
| Ken Edmundson | 2018-05-23 | Modifed call to bundleAdjustment->solveCholeskyBR() to return a raw pointer to a BundleSolutionInfo object. Am also deleting this pointer because jigsaw.cpp takes ownership from BundleAdjust. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2018-06-04 | (BundleXYZ modified on 2017-09-11) Added options for outputting and/or solving for body-fixed x/y/z instead of lat/lon/radius. References #501. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2018-06-04 | (BundleXYZ modified on 2017-09-17) Fixed a problem in the xml that was causing the input parameters to be omitted from the history. References #501. |
| Debbie A. Cook | 2018-06-04 | (BundleXYZ modified on 2018-03-18) Fixed a problem in the xml that excluded entry of values for latitudinal point sigmas when the coordinate type for reports was set to Rectangular and vice versa. References #501. |
| Tyler Wilson | 2019-05-17 | Cleaned up the bundleout.txt file and added new information in the header. Fixes #3267. |
| Aaron Giroux | 2019-12-19 | Added SCCONFIG parameter which allows users to pass in a pvl file with different settings for different instrumentIDs. Added logic into the observationSolveSettings function to construct BundleObservationSolveSettings objects based off of the settings in the pvl file. |
| Adam Paquette | 2020-12-23 | Added a warning when solving for target body radii/radius that is output to the application log. Updated the documentation to include the original rand notebook that jigsaw was based on. Also added a section in the documentation describing the target body radii solve issue. |
| Jesse Mapel and Kristin Berry | 2021-06-29 | Added the ability to bundle adjust images that use a CSM based model. New parameters CSMSOLVESET, CSMSOLVELIST, and CSMSOLVEYPE were added to specify which parameters to solve for. These parameters can also be used as keys in the SCCONFIG file. Modified images CSV file to generate a separate CSV for each sensor being adjusted. |
| Jesse Mapel | 2021-11-09 | Fixed measure residual reporting in bundleout.txt file to match the residuals reported in the residuals CSV file. |