ISIS Application Documentation
shadowtau | Standard View | TOC | Home |
Estimate optical depth (tau) using information from shadow measurements
Description
Categories
Groups
History
Description
This program estimates the optical depth (tau) values using a table file that consists of measurements collected at different locations on Level1 images with ISIS qview or another image display program. Information for different images can be entered into a single table file. The input values gathered are the average density measurements of a dark shadow and its photometric properties, and the average density of an unshadowed level-surface near the measured dark shadow on a Level1 image that are output to a table file. The table file contains one line per image point of the measured values separated by a comma or space in the following order:
- Image ID
- Incidence angle of the measured dark shadow
- Emission angle of the measured dark shadow
- Phase angle of the measured dark shadow
- The average DN (radiance) of a level unshadowed area
- The average DN (radiance) of a dark shadowed area
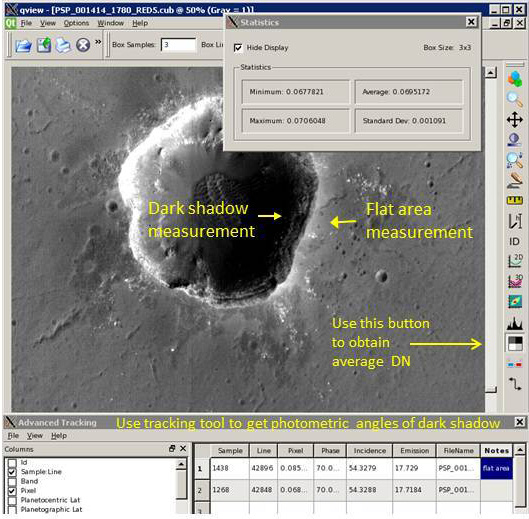
The image below shows an example of areas that could be measured on a
Level1 image using the qview tools. The tracking tool is used
to obtain the phase, incidence, and emission angles of the dark shadow.
The statistics tool in qview is used to obtain the
average density of the selected area on a dark shadow and an unshadowed
area near the dark shadow. The average pixel values can be added to the
tracking window, under notes, for each point, and saved to an output file.
Another option is to record the information using a text editor.
Whatever method is used to record the information into a table file, the input file to shadowtau must have required column information in a specific order. Note: the program qview does not output the photometric information in the correct order, so the user must modify the output before using the table file in shadowtau.
The following is an example of the input text file after it has been reordered:
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3287, 17.7148, 70.0486, 0.0943, 0.0667265
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3283, 17.7173, 70.0506, 0.0926, 0.0653045
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3191, 17.7427, 70.0657, 0.0888, 0.069008
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3716, 17.7178, 70.0861, 0.0888, 0.0506262
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3709, 17.7292, 70.0956, 0.091, 0.0518498
The following is the result of shadowtau; the bolded values are estimated
tau and albedo values, respectively:
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3287, 17.7148, 70.0486, 0.0943, 0.0667265, 0.43133, 0.120277
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3283, 17.7173, 70.0506, 0.0926, 0.0653045, 0.424314, 0.117599
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3191, 17.7427, 70.0657, 0.0888, 0.069008, 0.482241, 0.0944602
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3716, 17.7178, 70.0861, 0.0888, 0.0506262, 0.307933, 0.134256
PSP_001414_1780_RED5.cub, 54.3709, 17.7292, 70.0956, 0.091, 0.0518498, 0.311609, 0.138582
For each line in the table file above, the model results for the tau and albedo of the surface are appended to the end of the input line as shown in bold, and exported to the output file. All the results are based on user-selected photometric and atmospheric models, and either the default or user-modified parameter values. Most of the parameters default to appropriate values for Mars red filter images since it is the only other planet with modest atmospheric optical depths besides Earth. The results from the program are useful as an initial value for the "tau" parameter when a photometric correction is applied to the images.
The surface and atmosphere models use the same assumptions as the photomet photometric correction software, so the estimated optical depths are useful for processing images with that program. In other words, the optical depth calculated by this program is model-dependent; however, it is exactly the model-dependent value that will produce the most effective photometric correction in photomet.
SURFACE PHOTOMETRIC FUNCTION MODELS
| Name | Required parameter names |
|---|---|
| Hapkehen | B0, hg1, hg2, hh, theta, wh |
| Hapkeleg | Theta, wh, bh, ch, hh, b0, zerob0st |
| Lambert | None |
| LommelSeeliger | None |
| LunarLambert | L |
| LunarLambertEmpirical (Disabled until next release) | Datafile |
| LunarLambertMcEwen | None |
| Minnaert | K |
| MinnaertEmpirical (Disabled until next release) | Datafile |
| Name | Description | ISIS default | Valid range |
|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | Hapke opposition surge component | 0.0 | 0 <= value |
| Bh | Hapke Legendre coefficient for single particle phase function | 0.0 | -1 <= value <= 1 |
| Ch | Hapke Legendre coefficient for single particle phase function | 0.0 | -1 <= value <= 1 |
| Hg1 | Hapke Henyey Greenstein coefficient for single particle phase function | 0.213 | 0 <= value <= 1 |
| Hg2 | Hapke Henyey Greenstein coefficient for single particle phase function | 1.0 | 0 <= value <= 1 |
| Hh | Hapke opposition surge component | 0.0 | 0 <= value |
| K | Minnaert function exponent | 0.52 | 0 <= value |
| L | Lunar-Lambert function weight | 0.52 | No limit |
| Theta | Hapke macroscopic roughness component | 8.0 | 0 <= value <= 90 |
| Wh | Hapke single scattering albedo component | 0.52 | 0 < value <= 1 |
| Zerob0st | Flag to set opposition surge B0 to zero | True | True or False |
| Datafile | Input PVL file for empirical functions | None | String |
The functions are defined as follows, where phase is the phase angle, and u0 and u are the cosines of the incidence and emission angles, respectively:
- Lambert
- FUNC=u0
- LommelSeeliger
- FUNC=u0/(u0+u)
- Minnaert
- FUNC=u0**K * u**(K-1)
- LunarLambert (Lunar-Lambert, "lunar" part is Lommel-Seeliger)
- FUNC=(1-L)*u0 + 2*L*u0/(u0+u)
- MinnaertEmpirical
- FUNC=B(phase) * u0**K(phase) * u**(K(phase)-1)
- LunarLambertEmpirical
- FUNC=B(phase) * ((1-L)*u0 + 2*L*u0/(u0+u))
ATMOSPHERIC PHOTOMETRIC FUNCTION MODELS
| Function model name | Required parameters |
|---|---|
| Anisotropic1 | Bha, hnorm, wha |
| Anisotropic2 | Bha, hnorm, wha |
| HapkeAtm1 | Hga, hnorm, wha |
| HapkeAtm2 | Hga, hnorm, wha |
| Isotropic1 | Hnorm, wha |
| Isotropic2 | Hnorm, wha |
| Name | Description | ISIS Default | Valid Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bha | Coefficient of the single particle Legendre phase function | 0.95 | -1 <= value <= 1 |
| Hga | Coefficient of single particle Henyey Greenstein phase function | 0.7 | -1 < value < 1 |
| Hnorm | Atmospheric shell thickness normalized to the planet radius | 0.003 | 0 <= value |
| Wha | Single scattering albedo of atmospheric particles | 0.9 | 0 < value < 1 |
References: Chandrasekhar, S., 1960. Radiative Transfer. Dover, 393 pp. Hapke, B. W., 1981. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy 1: Theory. J. Geophys. Res., pp. 86,3039-3054. Hapke, B., 1984. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy 3: Corrections for macroscopic roughness. Icarus, 59, pp. 41-59. Hapke, B., 1986. Bidirectional reflectance spectroscopy 4: The extinction coefficient and the opposition effect. Icarus, 67, pp. 264-280. Johnson, J. R., et al., 1999, Preliminary Results on Photometric Properties of Materials at the Sagan Memorial Station, Mars, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 8809. Kirk, R. L., Thompson, K. T., Becker, T. L., and Lee, E. M., 2000. Photometric modelling for planetary cartography. Lunar Planet. Sci., XXXI, Abstract #2025, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston (CD-ROM). Kirk, R. L., Thompson, K. T., and Lee, E. M., 2001. Photometry of the martian atmosphere: An improved practical model for cartography and photoclinometry. Lunar Planet. Sci., XXXII, Abstract #1874, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston (CD-ROM). McEwen, A. S., 1991. Photometric functions for photoclinometry and other applications. Icarus, 92, pp. 298-311. Tanaka, K. L., and and Davis, P. A., 1988, Tectonic History of the Syria Planum Provice of Mars, J. Geophys. Res., 93, 14,893. Thorpe, T. E., 1973, Mariner 9 Photometric Observations of Mars from November 1971 through March 1972, Icarus, 20, 482. Tomasko, M. G., et al., 1999, Properties of Dust in the Martian Atmosphere from the Imager on Mars Pathfinder, J. Geophys. Res., 104, 8987
Categories
Related Objects and Documents
Applications
Parameter Groups
Files
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FROM | Input text file name |
| TO | Output text file name |
Photometric Model
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PHTNAME | Photometric model to be used |
| THETA | Macroscopic roughness angle |
| WH | Single scattering albedo |
| HG1 | Hapke Henyey Greenstein coefficient |
| HG2 | Hapke Henyey Greenstein Coefficient |
| BH | Hapke Legendre coefficient |
| CH | Hapke Legendre coefficient |
| HH | Hapke opposition surge |
| B0 | Hapke opposition surge |
| ZEROB0STANDARD | Specifies if opposition surge is set to zero under standard conditions |
| L | Lunar-Lambert function weight |
| K | Minnaert function exponent |
Atmospheric Model
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ATMNAME | Atmospheric model to be used |
| HGA | Henyey Greenstein coefficient |
| WHA | Single scattering albedo |
| BHA | Legendre coefficient |
| HNORM | Atmospheric shell thickness |
Files: FROM
Description
Input text file name with Image ID, incidence, emission, and phase angle of the measured dark shadow, average DN value of flat area and average DN value of a dark shadowed area
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | input |
| Filter | *.txt |
Files: TO
Description
Output text file name with the input ImageID, incidence, emission, and phase angle of the measured dark shadow, average DN value of flat area, average DN value of a dark shadowed area, plus the estimated tau (optical depth) and albedo (albedo of the surface) values appended to each input line.
| Type | filename |
|---|---|
| File Mode | output |
| Filter | *.txt |
Photometric Model: PHTNAME
Description
Specify the name of the surface photometric function model to apply
to the input image. The available options are the following:
- HAPKEHEN
-
Derive model albedo using the complete Hapke model with Henyey-Greenstein
single-particle phase function whose coefficients are hg1 and hg2,
plus single scattering albedo wh, opposition surge parameters hh and
b0, and macroscopic roughness theta. For a smooth model with opposition
effect use theta=0.
The table below shows the Hapke parameters for Mars from Johnson et al. (1999) for IMP data of Photometry Flats (soil) and may be reasonably representative of Mars as a whole. Note that (hg1, hg2=1.0) is equivalent to (-hg1, hg2=0.0).
Parameter settings for Mars Band Wh B0 Hh Hg1 Hg2 Red 0.52 0.025 0.17 0.213 1.0 Green 0.29 0.29 0.17 0.19 1.0 Blue 0.16 0.995 0.17 0.145 1.0 - HAPKELEG
- Derive model albedo using complete Hapke model with Henyey Legendre two-term Legendre polynomial phase function whose coefficients are bh and ch, plus single scattering albedo wh, opposition surge parameters hh and b0, and macroscopic roughness theta.
- LAMBERT
- A simple photometric model which predicts that light incident on a surface is scattered uniformly in all directions; the total amount of reflected light depends on the incidence angle of the illumination. This function does not depend upon the outgoing light direction.
- LOMMELSEELIGER
- This model takes into account the radiance that results from single scattering (scattering of collimated incident light) and does not take into account the radiance that results from multiple scattering (scattering of diffuse light which has made its way indirectly to the same position by being scattered one or more times). This model depends on the incidence and emission angles.
- LUNARLAMBERTMCEWEN
- This model was developed specifically for use with the Moon, and designed to be used in conjunction with the Moon(MoonAlbedo) normalization model.
- LUNARLAMBERTEMPIRICAL, LUNARLAMBERT, MINNAERTEMPIRICAL, and MINNAERT
- These models combine a weighted sum of the LommelSeeliger and Lambert models. Given a suitable value for the LunarLambert function weight, L, these models fit the true reflectance behavior of many planetary surfaces equally well as the Hapke model. These models also depend on the incidence and emission angles.
LUNARLAMBERTEMPIRICAL and MINNAERTEMPIRICAL photometric models, and the parameter name DATAFILE are disabled until the next release. There was a problem using the two functions listed above.
| Type | combo | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | HAPKEHEN | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internal Default | HAPKEHEN | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Photometric Model: THETA
Description
The "macroscopic roughness" of the surface as it affects the photometric behavior, used for Hapkehen or Hapkeleg. This is the RMS slope at scales larger than the distance photons penetrate the surface but smaller than a pixel. See Hapke (1986). The roughness correction, which is evaluated if theta is given any value other than 0.0, but is extremely slow. See Hapke (1986).
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (inclusive) |
| Maximum | 90.0 (inclusive) |
Photometric Model: WH
Description
The Hapke single scattering albedo of surface particles, see Hapke (1981).
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (inclusive) |
Photometric Model: HG1
Description
Asymmetry parameter used in Hapke Henyey Greenstein model for the scattering phase function of single particles in the surface. See Hapke (1981). The two-parameter Henyey Greenstein function is as follows:
P(phase)=(1-hg2) * (1-hg1**2)/(1+hg1**2+2*hg1*cos(phase))**1.5 + hg2 * (1-hg1**2)/(1+hg1**2-2*hg1*cos(phase))**1.5
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | -1.0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (exclusive) |
Photometric Model: HG2
Description
The Hapke Henyey Greenstein coefficient for single particle phase function. The second parameter of the two-parameter Henyey-Greenstein model for the scattering phase function of single particles in the surface. This parameter controls the proportions in a linear mixture of ordinary Heneyey Greenstein phase functions with asymmetry parameters equal to +hg1 and -hg1. See HG1 for the full formula.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (inclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (inclusive) |
Photometric Model: BH
Description
The Hapke Legendre coefficient for single particle phase function. A two-term Legendre polynomial is used for the scattering phase function of single particles in the surface:
P(phase) = 1 + bh * p1(cos(phase)) + ch * p2(cos(phase))Bh is not to be confused with the Legendre coefficient bha of the phase function for atmospheric particles, used when atmname=anisotropic1 or anisotropic2.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | -1.0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (exclusive) |
Photometric Model: CH
Description
The Hapke Legendre coefficient for single particle phase
function. A two-term Legendre polynomial is used for the scattering
phase function of single particles in the surface:
P(phase) = 1 + bh * p1(cos(phase)) + ch * p2(cos(phase))
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | -1.0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (exclusive) |
Photometric Model: HH
Description
The Hapke opposition surge component. The width parameter for the opposition effect for the surface if Hapkehen or Hapkeleg is used. See Hapke (1984).
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (inclusive) |
Photometric Model: B0
Description
The Hapke opposition surge component. The magnitude of the opposition effect for the surface if Hapkehen or Hapkeleg is used. See Hapke (1984).
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (inclusive) |
Photometric Model: ZEROB0STANDARD
Description
This specifies if the opposition surge component B0 is set to zero during the standard conditions phase. The program will automatically default to "true" if "ZEROB0STANDARD" is not defined by the user.
| Type | string | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | TRUE | |||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Photometric Model: L
Description
The Lunar Lambert function weight that governs limb-darkening in the lunar lambert photometric function:
Func=(1-L)*u0 + 2*L*u0/(u0+u)The values generally fall in the range from 0 (Lambert function) to 1 (Lommel-Seeliger or "lunar" function).
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
Photometric Model: K
Description
The Minnaert function exponent that governs limb-darkening in the Minnaert photometric function:
Func=u0**K * u**(K-1)The values generally fall in the range from 0.5 ("lunar-like", almost no limb darkening) to 1.0 (Lambert function).
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (inclusive) |
Atmospheric Model: ATMNAME
Description
This is the name of the atmospheric photometric function model to be
applied;the atmospheric model will be considered when the tau value is
calculated. The models ending with "1" use a first order scattering
approximation. Those ending with "2" use a second order scattering
approximation, and are slower but more accurate than the first order
scattering approximation. The atmospheric correction can be used with
only three atmospheric normalization models: albedoatm, shadeatm, and
topoatm. See Kirk et al. (2001).
The table below are photometric parameter values for Mars,
adopted from Tomasko et al. (1999):
| Band | Wha | Hga |
|---|---|---|
| Red | 0.95 | 0.68 |
| Blue | 0.76 | 0.78 |
| Type | combo | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Default | HAPKEATM1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Internal Default | HAPKEATM1 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Option List: |
|
Atmospheric Model: HGA
Description
The coefficient of single particle Henyey Greenstein phase function. Henyey-Greenestein asymmetry parameter for atmospheric particle phase function, used in hapkeatm1 and hapkeatm2 atmospheric models. Not to be confused with corresponding parameter hg1 for the surface particles.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | -1.0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (exclusive) |
Atmospheric Model: WHA
Description
The single scattering albedo of atmospheric particles.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (exclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (inclusive) |
Atmospheric Model: BHA
Description
The coefficient of the single particle Legendre phase function. Coefficient of p1 (cosine) term of atmospheric particle phase function, used in anisotropic1 and anisotropic2 atmospheric models. Not to be confused with corresponding coefficient bh for the surface particles.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | -1.0 (inclusive) |
| Maximum | 1.0 (inclusive) |
Atmospheric Model: HNORM
Description
The atmospheric shell thickness normalized to the planet radius, used to modify angles to get more accurate path lengths near the terminator (Ratio of scale height to the planetary radius). The hnorm parameter is defined as "0.003" for Mars, which is the only planet for which the atmospheric modes are currently used.
| Type | string |
|---|---|
| Default | None Specified |
| Internal Default | None Specified |
| Minimum | 0.0 (inclusive) |
History
| Randy Kirk | 1999-11-27 | USGS Flagstaff Original Version |
| Sharmila Prasad & Janet Barrett | 2011-09-04 | Isis3 Original version, shadow_tau ported from isis2 to shadowtau in isis3 |
| Janet Barrett | 2012-01-05 | Tested code to make sure it gives the same results as the ISIS2 version. Created app tests. |
| Ella Mae Lee | 2012-11-20 | Improve shadowtau documentation, change ZEROB0STANDARD to ZEROB0ST, modified remaining ISIS2 parameter values to ISIS3 values, and disabled the use of a datafile with the empirical functions because of a bug in the program, fixes #455. |
| Janet Barrett | 2012-12-07 | PLEASE NOTE (in reference to change made on 2012-11-20): The backwards compatibility for the shorter ZEROB0ST parameter name has not been fully implemented in ISIS. As a result, this change has been removed and the full ZEROB0STANDARD parameter name must be used. Support for aliases (deprecated values) must be fully implemented in ISIS before the shorter parameter name (ZEROB0ST) will be available. Fixes #1288. |
| Lynn Weller | 2013-02-25 | Removed links to applications imbedded in text and replaced with italicized application name. Added application links to the "Related Objects and Documents" section of the documentation. Fixes mantis ticket #1525. |
| Kimberly Oyama and Janet Barrett | 2013-04-10 | Removed the "NONE" option from the "ATMNAME" parameter because an atmospheric model is required for calculating tau. Fixes #1313. |